Discover the surprising trends in Covid booster vaccine uptake in the U.S. Learn about the factors contributing to low booster rates and the implications for public health. The Covid-19 pandemic has been a defining event of the 21st century, reshaping our lives in unprecedented ways. As the world grappled with the virus, vaccines emerged as a beacon of hope, promising to curb the spread and severity of the disease. Among these vaccines, booster doses have played a crucial role in enhancing immunity and providing continued protection against emerging variants. However, the uptake of Covid booster vaccines in the United States has revealed some surprising and concerning trends.
The Importance of Booster Vaccines
Booster vaccines are designed to “boost” the immune response that may have waned since the initial vaccination. They are particularly important in the context of Covid-19, as the virus continues to mutate, leading to new variants that can partially evade immunity. Booster doses help to reinforce the body’s defenses, ensuring that individuals remain protected against severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
Initial Enthusiasm and Subsequent Hesitation

When Covid-19 vaccines were first rolled out, there was a wave of enthusiasm and relief. Millions of Americans lined up to receive their shots, eager to protect themselves and their loved ones. However, as the pandemic progressed and booster doses became available, the initial enthusiasm began to wane. Despite the clear benefits of booster vaccines, a significant portion of the population has been hesitant to receive them.
Statistics on Booster Uptake
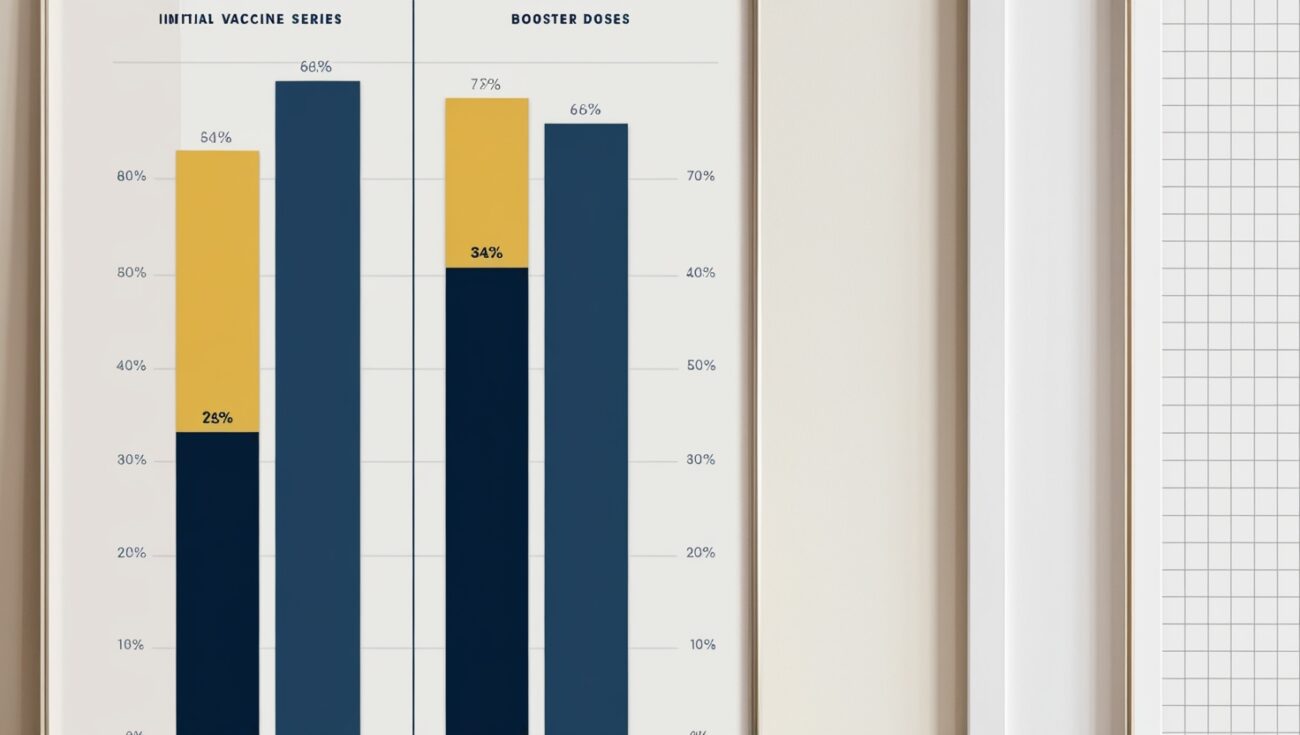
Recent data reveals a stark reality: a surprisingly low number of Americans have opted to receive their Covid booster vaccines. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), as of November 2024, only about 40% of eligible Americans have received a booster dose. This figure is significantly lower than the initial vaccination rates, which saw over 70% of the population receiving their primary series of Covid-19 vaccines.
Factors Contributing to Low Uptake

Several factors contribute to the low uptake of Covid booster vaccines in the United States:
- Vaccine Fatigue: After multiple rounds of vaccinations, some individuals are experiencing vaccine fatigue. The repeated messaging about the importance of vaccines, coupled with the ongoing pandemic, has led to a sense of exhaustion and complacency.
- Misinformation and Mistrust: The spread of misinformation about vaccines has been a persistent issue throughout the pandemic. False claims about the safety and efficacy of booster doses have fueled mistrust and skepticism among certain segments of the population.
- Perceived Risk: As the immediate threat of Covid-19 appears to diminish, some individuals perceive the risk of infection as lower and may not see the need for a booster dose. This perception is particularly prevalent among younger, healthier individuals who believe they are less likely to experience severe illness.
- Access and Convenience: Access to booster vaccines can be a barrier for some individuals, particularly those in rural or underserved areas. Additionally, the convenience of getting a booster dose, including the availability of appointments and proximity to vaccination sites, can impact uptake.
- Policy and Communication: Inconsistent messaging and policy changes regarding booster doses have also contributed to confusion and hesitancy. Clear, consistent communication from public health authorities is essential to encourage booster uptake.
The Role of Public Health Campaigns

Public health campaigns play a vital role in addressing the factors contributing to low booster uptake. Effective campaigns should focus on:
- Education and Awareness: Providing accurate, evidence-based information about the benefits and safety of booster vaccines is crucial. Public health authorities should work to dispel myths and misinformation through targeted education campaigns.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with communities, particularly those with lower vaccination rates, can help build trust and address specific concerns. Community leaders, healthcare providers, and trusted figures can play a key role in promoting booster vaccines.
- Accessibility and Convenience: Efforts should be made to ensure that booster vaccines are easily accessible to all individuals. This includes expanding vaccination sites, offering flexible appointment times, and providing mobile vaccination units in underserved areas.
- Clear Communication: Consistent and clear communication from public health authorities is essential. Messaging should emphasize the importance of booster doses in maintaining immunity and protecting against new variants.
The Impact of Low Booster Uptake
The low uptake of Covid booster vaccines has significant implications for public health. Without widespread booster coverage, the population remains vulnerable to new variants of the virus. This can lead to increased transmission, higher rates of severe illness, and greater strain on healthcare systems. Additionally, low booster uptake can hinder efforts to achieve herd immunity, prolonging the pandemic and its associated social and economic impacts.
Lessons Learned and the Path Forward

The experience with Covid booster vaccines offers valuable lessons for future public health initiatives. It highlights the importance of addressing vaccine fatigue, combating misinformation, and ensuring equitable access to vaccines. Moving forward, public health authorities must continue to adapt their strategies to meet the evolving challenges of the pandemic.
Conclusion
The uptake of Covid booster vaccines in the United States has revealed a complex interplay of factors influencing public health behavior. While the initial rollout of vaccines was met with enthusiasm, the subsequent booster campaigns have faced significant hurdles. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including education, community engagement, accessibility, and clear communication. By learning from these experiences, we can better prepare for future public health crises and ensure that all individuals have the protection they need.

